A Deep Study the Aluminum Casting Process: From Layout to Finished Item
The light weight aluminum Casting process encompasses several crucial stages, each requiring accuracy and competence. It begins with the style phase, where ideas develop into detailed specifications. The preparation of mold and mildews adheres to, utilizing numerous casting methods. After melting and putting, the cooling stage determines the final properties of the light weight aluminum. The trip doesn't finish there; completing processes play a considerable duty in accomplishing high quality standards. What happens next in this elaborate process?
Recognizing Light Weight Aluminum Spreading
Aluminum Casting is an essential procedure in producing that entails putting liquified aluminum into a mold to create numerous forms and parts. This approach is preferred for its capacity to generate complex styles with exceptional dimensional precision. The process begins with choosing top quality aluminum alloys, which are then melted at elevated temperature levels. As soon as in a fluid state, the aluminum is thoroughly put into molds, which can be made from sand, metal, or various other products, depending on the desired end product.
Air conditioning takes place as the molten aluminum solidifies, developing the preferred form. After cooling down, the castings are removed from the molds and undertake ending up procedures such as machining or surface area treatment to improve their homes and look. Recognizing aluminum Casting not only highlights its relevance in design and manufacturing however additionally emphasizes its convenience in producing light-weight, resilient parts for various industries, including automobile, aerospace, and durable goods.
The Design Process: From Concept to CAD
The design process for aluminum Casting begins with preliminary principle development, where ideas are transformed into concrete requirements. Following this stage, CAD modeling techniques are utilized to create accurate digital representations of the styles. This change from principle to CAD is vital for making sure precision and usefulness in the Casting process.
Initial Idea Advancement
Launching the style procedure for light weight aluminum Casting includes changing abstract ideas right into substantial principles. This phase is basic, as it prepares for effective product advancement. Developers team up with stakeholders and designers to specify the functional needs and aesthetic elements of the spreading. Brainstorming sessions typically generate several ideas, which are after that assessed for manufacturability, cost-effectiveness, and expediency. Illustrations and preliminary designs may be developed to visualize possible layouts. Comments from employee and customers is vital in fine-tuning these ideas. Repetitive conversations aid to recognize possible challenges, guaranteeing that the last design lines up with both technical specifications and customer requirements. Ultimately, this phase sets the phase for the change from idea to more comprehensive digital depictions.
CAD Modeling Techniques
As the layout procedure changes from preliminary principles to detailed representations, CAD modeling strategies become crucial tools for developers and designers. These strategies allow for the development of specific, scalable electronic models that precisely mirror the desired physical item. Typical approaches consist of 3D strong modeling, surface modeling, and parametric style, each offering one-of-a-kind abilities for various task needs. Engineers use software like AutoCAD, SolidWorks, and CATIA to fine-tune layouts, simulate performance, and recognize possible issues before manufacturing. The assimilation of CAD with other innovations, such as finite aspect evaluation (FEA), boosts the design process additionally by forecasting material habits under stress. Eventually, reliable CAD modeling streamlines interaction among team participants and improves the general performance of the aluminum Casting procedure.
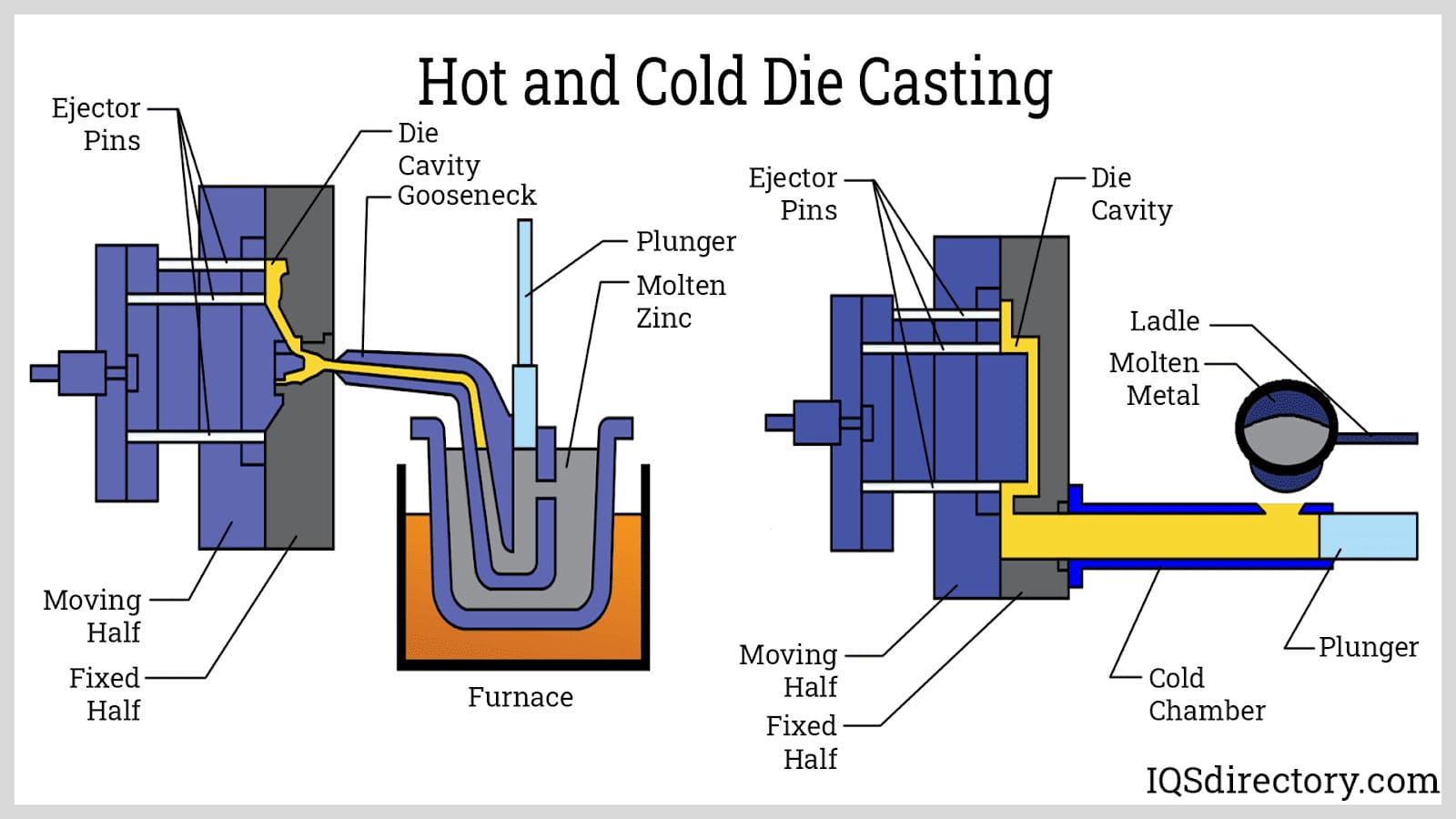
Preparing the Mold And Mildew: Sand, Die, and Investment Spreading
When preparing molds for aluminum spreading, the option of technique greatly affects the end product's top quality and accuracy. 3 key techniques are typically made use of: sand spreading, pass away casting, and investment spreading.
Sand Casting involves creating a mold from sand, which is functional and economical, making it appropriate for huge components and complicated geometries. This technique, nonetheless, might generate a rougher surface area coating contrasted to various other strategies.
Pass away casting uses steel molds, making it possible for high-volume manufacturing and exceptional dimensional accuracy. This approach is excellent for creating elaborate layouts with limited tolerances and smooth surface areas however calls for higher ahead of time expenses as a result of mold manufacture.
Investment spreading, also called lost-wax casting, gives exceptional accuracy and surface coating, making it suitable for intricate parts. This technique entails producing a wax pattern, which is covered in ceramic, enabling fine information throughout the Casting process. Each method has its benefits, influencing the casting's qualities and applications.
Pouring and thawing Light weight aluminum: Methods and Tools
In the aluminum Casting procedure, effective melting and pouring strategies are crucial for accomplishing high-quality results. Numerous melting techniques and specialized putting equipment play a substantial role in ensuring ideal fluidness and temperature control - Aluminum Casting Manufacturer. Understanding these basics is important for both amateur and skilled shop professionals
Melting Methods Review
A variety of melting methods are utilized in the light weight aluminum Casting process, each customized to particular applications and manufacturing scales. Usual approaches include crucible melting, where light weight aluminum is heated in a ceramic or metal container, frequently ideal for little batches. Induction melting makes use of magnetic fields to warmth aluminum quickly and effectively, ideal for larger manufacturing requirements. Electric arc furnaces supply a high-temperature setting, making them appropriate for reusing aluminum scrap. In addition, rotating heating systems provide a continual melting process, improving productivity. Each method has its advantages, such as power performance, melting rate, and worldly top quality, ensuring that suppliers can Recommended Site choose one of the most appropriate method based on their functional demands and wanted outcomes in the Casting procedure.
Putting Tools Basics
Following the melting procedure, effective putting tools plays a significant role in ensuring the successful transfer of liquified aluminum into mold and mildews. Secret parts consist of ladles, pouring mugs, and automated pouring makers. Ladles, generally constructed from heat-resistant materials, are created to hold and transfer liquified aluminum securely. Pouring cups boost control during the transfer, promoting a stable put to minimize disturbance and oxidation. Automated pouring makers are increasingly prominent, assuring consistent circulation prices and decreasing human mistake. These makers can be programmed for accuracy, optimizing casting high quality. In addition, temperature tracking tools are important to ensure the liquified light weight aluminum remains within the ideal temperature variety, additional boosting the top quality of the final cast product. Appropriate choice and upkeep of putting tools are vital for efficiency and security.
Cooling and Solidification: Changing Liquid to Solid
Air conditioning and solidification play a vital role in the light weight aluminum Casting procedure, as they identify the last residential properties of the cast steel. After pouring, the liquified aluminum starts to lose warmth, moving from fluid to solid. This cooling stage is vital, see this site as it influences mechanical residential properties such as microstructure, strength, and ductility. The price of cooling can differ based upon elements such as mold and mildew material, density, and environmental problems. Quick cooling might cause a finer grain structure, improving toughness, while slower cooling can bring about coarser grains, impacting ductility.
In addition, consistent cooling is vital to avoid issues such as warping or breaking. As the steel solidifies, the development of dendrites takes place, which are tree-like structures that impact the general honesty of the casting. Comprehending the air conditioning and solidification dynamics enables designers and shop workers to optimize the procedure, making certain that the end product satisfies the essential specs and top quality standards.

Ending Up Processes: Machining, Covering, and Inspection
Ending up processes are critical in refining light weight aluminum castings to fulfill rigid specifications and boost performance. These procedures normally include covering, machining, and examination, each playing a critical function in achieving the preferred quality.
Machining includes getting rid of excess material from the Casting to acquire exact dimensions and surface area coatings. Methods such as milling, transforming, and grinding are commonly utilized to assure that the end product fulfills style tolerances.
Finish serves to shield the light weight aluminum surface from environmental aspects, enhancing corrosion resistance and aesthetic allure. Alternatives include anodizing, powder finishing, and paint, each offering distinctive advantages depending upon the application.
Examination is important to confirm that the ended up spreadings meet quality requirements. Approaches such as aesthetic inspection, dimensional checks, and non-destructive testing are utilized to identify any flaws. With each other, these completing procedures assure that aluminum spreadings are reliable, long lasting, and all set for their desired applications.
Applications of Aluminum Castings in Different Industries

The customer products market includes light weight aluminum spreadings in products like kitchenware and home appliances, exploiting on their thermal conductivity and resilience. The building market utilizes aluminum spreadings in window frames, doors, and decorative elements, boosting aesthetic appeals while maintaining capability. Furthermore, the marine market counts on aluminum spreadings over here for watercraft parts, where resistance to deep sea corrosion is crucial. Overall, aluminum castings give innovative services throughout various applications, making them vital in modern manufacturing procedures.
Frequently Asked Concerns
What Are the Ecological Impacts of Aluminum Casting?
The ecological influences of light weight aluminum Casting consist of energy-intensive manufacturing, greenhouse gas emissions, and prospective water pollution. In addition, mining bauxite for aluminum adds to habitat devastation, while recycling initiatives can minimize some adverse effects.
Exactly How Does Light Weight Aluminum Casting Compare to Other Metal Casting Procedures?
Light weight aluminum casting typically provides advantages like light-weight residential properties and rust resistance contrasted to other metal Casting processes. It may have constraints in strength and temperature resistance, making its viability dependent on certain application requirements.
What Safety And Security Safety Measures Are Necessary Throughout Aluminum Spreading?
During aluminum spreading, security preventative measures include putting on protective equipment, guaranteeing correct ventilation, keeping equipment, and complying with strict procedures to handle liquified steel. These procedures aim to decrease dangers such as burns, breathing of fumes, and devices breakdowns.
Can Aluminum Castings Be Recycled After Use?
Aluminum spreadings can undoubtedly be recycled after usage. The reusing process maintains the product's properties, making it a lasting alternative. This practice substantially decreases waste and preserves power, promoting environmental duty in manufacturing markets.
What Are Usual Defects in Light Weight Aluminum Castings and Their Reasons?
Common problems in light weight aluminum castings include porosity, cool shuts, and shrinkage - Aluminum Casting Manufacturer. These problems often develop from poor melting temperatures, improper mold layout, and insufficient air conditioning rates, affecting the total high quality and efficiency of the end product
Light weight aluminum Casting is a vital process in manufacturing that includes pouring liquified aluminum right into a mold and mildew to create different forms and components. The style procedure for aluminum Casting starts with initial principle growth, where ideas are transformed into substantial specs. Starting the design process for aluminum Casting entails transforming abstract ideas right into tangible concepts. In the aluminum Casting procedure, reliable melting and pouring techniques are vital for accomplishing top quality results. A selection of melting techniques are utilized in the light weight aluminum Casting procedure, each tailored to certain applications and production ranges.